Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring
Who should not undergo calcium scoring?
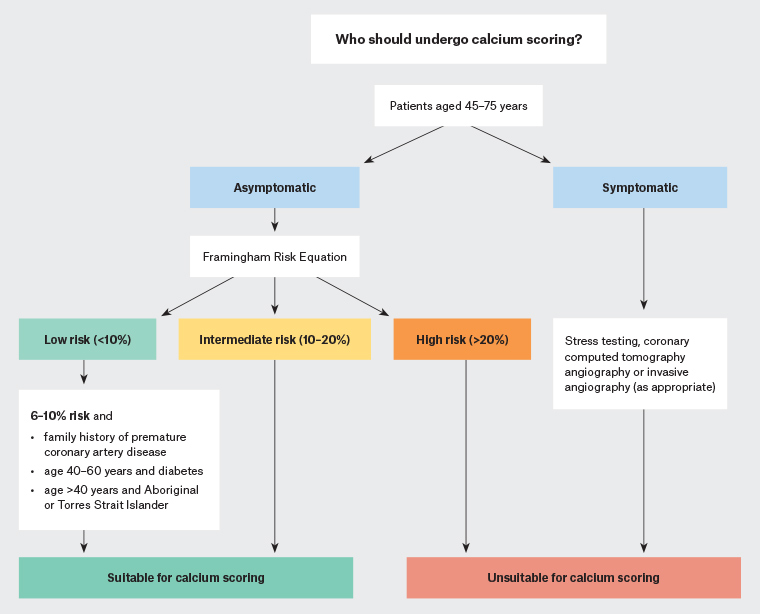
The CSANZ recommends against calcium scoring for high-risk and very low–risk patients (<6% 10-year risk), for whom calcium scoring has a limited ability to reclassify cardiovascular risk.3 The use of calcium scoring for symptomatic patients is also not recommended
Who should consider a CAC scan?
- Individuals with a moderate risk of heart disease, particularly those between the ages of 40 and 70 with risk factors like a family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure, smoking, overweight or obesity, or physical inactivity, may benefit from CAC scoring.
- It can also be considered in younger individuals (<40) with a strong family history of hypercholesterolemia.
- According to CardioSmart – American College of Cardiology (2018), CAC scoring is most helpful when there is uncertainty about whether a statin (cholesterol-lowering medication) should be started.
Who should avoid a CAC scan?
- Pregnant women should avoid CAC scans due to the radiation exposure, which could be harmful to the fetus.
- CAC scoring may not be helpful for individuals who already have a diagnosis of coronary artery disease, are exhibiting symptoms of CAD, have already undergone treatment for CAD, or are already classified as high-risk or very low-risk for heart disease.
Benefits and limitations
- Benefits: CAC scoring is a non-invasive, quick, and painless procedure that can aid in the early detection of CAD risk, guide treatment decisions, and enhance personalized treatment plans. Studies suggest it can improve risk stratification over traditional risk calculators alone.
- Limitations: It involves a small amount of radiation exposure. It primarily detects calcified plaque, and does not provide information about non-calcified (soft) plaque. It may not be covered by all insurance plans. The significance of moderate CAC scores in predicting prognosis and guiding treatment is still under investigation.
It is important to discuss your individual risk factors and the potential benefits and limitations of CAC scoring with your doctor to determine if this test is appropriate for you.




